Ash wastewater spill at northern Minnesota coal plant more than five times larger than first reported
Last edited Sun Jul 21, 2024, 04:36 AM - Edit history (1)
A coal ash wastewater leak at a northern Minnesota power plant earlier this week was more than five times larger than original estimates, according to Duluth-based Minnesota Power and the Minnesota Pollution Control Agency.
The utility initially reported about a million gallons of wastewater leaked out of an underground pipe late Tuesday morning at its Boswell Energy Center in Cohasset near Grand Rapids. Now Minnesota Power and the MPCA say about 5.5 million gallons escaped.
Preliminary modeling shows increased levels of sulfate and boron in the area where the wastewater entered a creek that flows into Blackwater Lake, an impoundment on the Mississippi River.
...
The leak occurred from an underground pipeline that transfers wastewater from an inactive settling pond that stored ash from coal combustion. The utility used the water in the plant for dust and temperature control.
The spill occurred on land, but a portion of the wastewater flowed to Blackwater Creek and into Blackwater Lake.
Emphasis added. More:
https://www.mprnews.org/story/2024/07/19/ash-wastewater-spill-at-northern-minnesota-coal-plant-more-than-five-times-larger-reported
Google says an Olympic swimming pool holds 660,000 gallons. So 5.5 million gallons is 8.33 Olympic swimming pools.
The Boswell plant is slated to quit generating from the last 2 units in 2030 and 2035 respectively.
Coal was about 9% of U.S. energy consumption in 2023, compare to 36% from natural gas
https://www.eia.gov/energyexplained/us-energy-facts/
Fossil fuels total to 84%. Wind & Solar only 2.6%. Other renewables only 6.4% (most of that is biomass). Nuclear: 9%
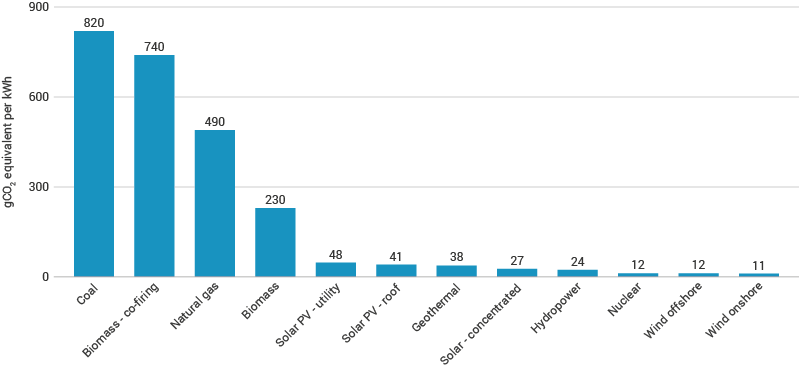
Coal is a big standout as far as carbon emissions - 1.67 times as bad as natural gas per KWH of electricity produced
https://world-nuclear.org/information-library/energy-and-the-environment/carbon-dioxide-emissions-from-electricity